XDailyDialog
XDailyDialog: A Multilingual Parallel Dialogue Corpus
This repository includes the dataset and baseilnes of the paper: “XDailyDialog: A Multilingual Parallel Dialogue Corpus”. You can also visit this website of XDailyDialog to see details.
Authors: Zeming Liu, Ping Nie, Jie Cai*, Haifeng Wang, Zheng-Yu Niu, Peng Zhang, Mrinmaya Sachan, Kaiping Peng
What’s New
- 2023/05/15 Update knn-chat train prosedure.
- 2023/05/13 Add knn-chat first train step.
- 2023/05/12 Update datesets full version.
We created this multilingual parallel dialogue corpus based on the popular english dialogue dataset: DailyDialog: A Manually Labelled Multi-turn Dialogue Dataset
1. Abstract:
High-quality corpora are significant to the development of dialogue models. However, most existing corpora for open-domain dialogue modeling are limited to a single language. The absence of multilingual open-domain dialog corpora not only limits the research on multilingual or cross-lingual transfer learning but also hinders the development of robust open-domain dialogue systems that can be deployed in other parts of the world. In this paper, we provide a multilingual parallel open-domain dialog dataset, XDailyDialog to enable researchers to explore the challenging task of multilingual and cross-lingual open-domain dialogue. XDailyDialog includes 13K dialogues aligned across 4 languages (52K dialogues and 410K utterances in total). We then propose a dialogue generation model, kNN-Chat, which has a novel kNN-search mechanism to support unified response retrieval for monolingual, multilingual, and cross-lingual dialogue. Experiment results show the effectiveness of this framework.
2. Dataset
Data are available in data folder. Dialogues, topics, emotion, and action labels are in the same format as DailyDialog: A Manually Labelled Multi-turn Dialogue Dataset. We provide manually labeled dialogues_text_De for German, dialogues_text_It for Italian, and dialogues_text_Zh for the Chinese version. All files in the data folders are:
ls ./data
data/
├── 1k_part_data
│ ├── dialogues_action.txt
│ ├── dialogues_emotion.txt
│ ├── dialogues_text_De.txt
│ ├── dialogues_text_En.txt
│ ├── dialogues_text_It.txt
│ ├── dialogues_text_Zh.txt
│ └── dialogues_topic.txt
├── dataset.py
├── dialogues_action.txt
├── dialogues_emotion.txt
├── dialogues_text_De.txt
├── dialogues_text_En.txt
├── dialogues_text_It.txt
├── dialogues_text_Zh.txt
└── dialogues_topic.txt
3. Basic Statistics
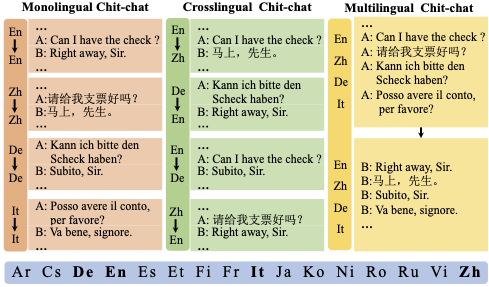
The developed XDailyDialog dataset contains 52,472 Manually Labeled multi-lingual multi-turn dialogues for four languages (English, Chinese, German, Italian). English data comes from DailyDialog: A Manually Labelled Multi-turn Dialogue Dataset.
4. Requirements
To run baselines, python libraries below are needed.
- sentencepiece 0.1.96
- datasets 1.8.0
- transformers 4.7.0
- jieba 0.42.1
- nltk 0.8.1
- sacrebleu 2.3.1
5. Preprocess
run parser.py to convert original txt data into Monolingual, Multi-lingual, and Cross-lingual settings. Then run split.py to split data into train, dev and test. Then we need to run preprocess.py to process our txt data from different tasks into standard datasets input format, you also need to put our tasks txt data in./data/raw/ like:
python parser.py
python preprocess.py
data
├── crosslingual
│ ├── De_En
│ ├── En_De
│ ├── En_Zh
│ └── Zh_En
├── dataset.py
├── monolingual
│ ├── De
│ ├── En
│ ├── It
│ └── Zh
├── multilingual
│ ├── dev.jsonl
│ ├── test.jsonl
│ └── train.jsonl
├── raw
│ ├── crosslingual
│ ├── monolingual
│ └── multilingual
run our preprocess.py. Then you will get the preprocessed data in ./data like above.
python preprocess.py
6. Reproduce Baselines
you can run run.bash to reproduce our results.
sh run.bash 0 data/monolingual/It
0 means the gpu=0 and data/monolingual/It is the data directory we want to train and evaluate our model. You can change model names in run.bash to run different models.
Parameters in run.bash:
export PYTHONIOENCODING=utf8
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$1 # gpu number
WORKING_DIR=./ #your work dir where run.bash is in.
DATA_NAME=$2 # "data/monolingual/En", task name, and corresponding directory.
EPOCHS=5
BATCH_SIZE=4
EVAL_BATCH_SIZE=4
GRAD_ACC=2
LR=2e-5
MODEL="mt5-base" # model name
# CKPT_PATH="${WORKING_DIR}/checkpoints/mt5-base/"
CKPT_PATH="google/mt5-base"
SAVE_PATH="${WORKING_DIR}/results/${DATA_NAME}/${MODEL}/ep${EPOCHS}_bs${BATCH_SIZE}_lr${LR}_G${GRAD_ACC}"
OPTS=" --model_name_or_path ${CKPT_PATH} \
--data_path ${WORKING_DIR} \
--data_name ${DATA_NAME} \
--output_dir ${SAVE_PATH} \
--max_source_length 512 \
--max_target_length 200 \
--val_max_target_length 200 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--do_predict \
--num_train_epochs ${EPOCHS} \
--per_device_train_batch_size ${BATCH_SIZE} \
--per_device_eval_batch_size ${EVAL_BATCH_SIZE} \
--gradient_accumulation_steps ${GRAD_ACC} \
--learning_rate ${LR} \
--logging_steps 500 \
--evaluation_strategy epoch \
--save_strategy epoch \
--warmup_steps 500 \
--disable_tqdm False \
--load_best_model_at_end True \
--metric_for_best_model bleu-2 \
--save_total_limit 2"
7. Reproduce knn-chat results
Firstly, you need to download the original mbart model file:
cd knn-chat
sh download_mbart.sh
After executing the above command, the corresponding mbart model will be downloaded to the local directory.
Then, it is necessary to preprocess the specific types of data using the corresponding tokenization methods of mbart.
sh preprocess_data.sh monolingual En
monolingual means the TYPE=monolingual and En means the LAN=En type.
The combination of TYPE and LAN can be found from the following combinations:
TYPE=monolingual LAN=En, It, De, or Zh
TYPE=crosslingual LAN=En-DE, ``, De, or Zh
TYPE=multilingual LAN=En, It, De, or Zh
After preprocessing, fine-tuning can be started. Finetune mbart model can be done in two ways:
- Through the huggingface Transformers framework.
- Through the fairseq framework.
The following examples are fine-tuned through the fairseq framework:
sh run_finetune.sh
After finetuning, it is necessary to use the Finetuned model to construct the faiss index and datastore.
sh create_data_store.sh
sh build_faiss_index.sh
Based on the results of the above construction, you can train the KNN-Chat model we need.
sh train_knn-mt_model.sh
8. License
Apache License 2.0 and CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
Since DailyDialog dataset is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. Note the dataset may not be adopted for commercial use.